Abstract
Aims: The absolute number of chronic phase CML patients (pts) reaching the treatment-free remission (TFR) criteria has been substantially increased by the use of second-generation TKI (TKI2), initiated since diagnosis, comparing to Imatinib first-line. However, the relative rate of unsuccessful TFR (i. e. pts loosing their MMR after TKI2 cessation) still remains around 50% at 2 years and beyond, whatever the TKI2 was. The aim of this study is to analyse the rate of successful TFR in pts receiving Nilotinib (Nilo) or Dasatinib (Dasa) first-line obtaining the appropriate criteria.
Methods: Observational retrospective study in 3 reference centers of the French group of CML lead between 2010 and 2021. Eligible pts were CP CML pts initiating either Nilo 300 mg BID or Dasa 100 mg daily since diagnosis, until cessation for sustained MR4.5 (i.e. ≥2 years on ≥4 datapoints). Data were retrospectively collected according to the national regulations with pts' information. All pts were assessed and followed according to ELN recommendations 2009, 2013 and 2020 along treatment and to the recommendations from the French group of CML (D. Rea et al., Cancer 2018) for TFR. In this regard, the TKI2 was resumed in case of loss of MMR. All BCR-ABL1 assessments were performed in the 3 reference laboratories, standardised and expressed in % (IS) with ≥32,000 copies of ABL1 as control. All patients were harbouring major BCR-ABL1 transcripts. The primary endpoint was the survival without loss of MMR after TKI2 cessation. The secondary endpoints were the kinetics of MMR loss, and the identification of factors influencing MMR loss.
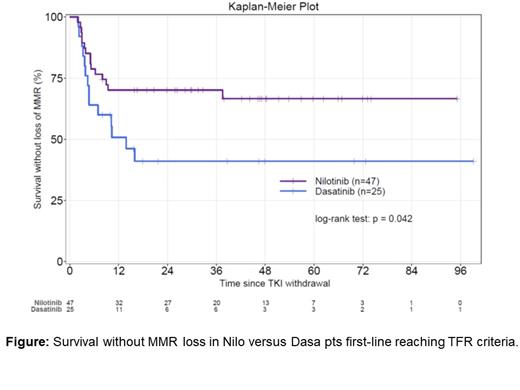
Results: Seventy-two pts were reported (47 Nilo, 25 Dasa) with 57% females with a median age at diagnosis of 48 (36.75-61.25) years. The median follow-up since diagnosis was 9.26 (3.75-13.75) years (8.8 for Nilo and 9.47 for Dasa p=ns) and after TKI2 cessation 3.94 (0.7-8.8) years (3.92 for Nilo and 3.90 for Dasa p=ns). Sokal scores were 42% Low, 41% Intermediate, 17% High in Nilo and 39% L, 25% I and 35% H in Dasa pts (p=ns). ELTS scores were 50% L, 22% I, 9.5% H (18.5% Uk) in Nilo and 46.5% L, 28.5% I and 3.5% H (21.5% Uk) in Dasa pts (p=0.95). Five (9%) pts harboured ACA at diagnosis in the Nilo group and 2 (7%) in the Dasa group (p=1.00). The median time from TKI2 initiation to sustained MR4.5 was 19 (3.12-36) months in the Nilo group and 16 (6.3-39) months in the Dasa group (p=0.644). The duration of sustained MR4.5 until cessation was 3.04 (1.5-9.3) years for Nilo and 2.65 (1.11-7.95) for Dasa (p=0.96). The median dosing of Nilo was 600 (300-800) mg daily and 80 (20-100) mg at TKI2 cessation. None of these patients switched to another TKI during the follow-up. TKI2 cessation occurred after 60.5 (43-74.5) months in the Nilo group and 68 (39-90) months in the Dasa group (p=0.581). Thirty-seven pts out of 47 (79%) were BCR-ABL1 undetectable at Nilo cessation 18/25 (72%) at Dasa cessation (p=0.60). At M3 after discontinuation, 58% of pts remained undetectable after Nilo cessation and 30.4% after Dasa cessation (p=0.05).The median survival of pts without loss of MMR was not reached in the Nilo group, and was 14 (4.73-NR) months in the Dasa group, (p=0.042) as analysed by the KM method (Figure 1.). Two patients died (1 Nilo, 1 Dasa) from competing events (solid tumours) after unsuccessful TFR.
Twenty-eight pts (14 Dasa, 14 Nilo) restarted their TKI2 after MMR loss and all regained ≥ MMR after 3 months of Dasa at a median dose of 75 (40-100) mg daily and all except one (who regained MMR at M12) after resumption of Nilo at a median dose of 350 (300-600) mg daily.
Univariate analysis identified pts with H+I Sokal (as compared to low) as an unfavourable factor for successful TKI2 cessation [HR=0.35 (0.15-0.83), p=0.017] and type of TKI2 (Nilo as reference vs Dasa) was discriminant [HR=2.1 (1.01-4.35), p=0.047]. Multivariate analysis identified the type of TKI2 as a significant factor impacting on TFR outcome [HR 2.11 (0.97-4.55], p=0.05].
Conclusions: As it is likely that no prospective head-to-head comparison will be performed in this setting, on this limited series of pts, we conclude that the outcome of TFR seems to be different according to the TKI2 used since diagnosis, suggesting the impact of distinct biological variables modified by the type of TKI2 on the long run (such as immunological system, BM micro-environment, others) on TFR outcome.
Nicolini: Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding; Kartos Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sun Pharma Ltd.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria; Incyte Biosciences: Honoraria, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Etienne: Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Rea: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal